Ever wondered how Uncle Sam determines the salaries of his vast workforce? The General Schedule (GS) pay scale is the backbone of federal compensation, a complex system that has evolved significantly over time. Understanding the GS pay scale history is crucial for anyone working within the federal government or considering a career in public service. This deep dive will unpack the origins, development, and current state of the GS system, exploring its nuances and impact.
The GS pay scale's roots can be traced back to the Classification Act of 1923, which aimed to standardize federal positions and salaries based on the principle of "equal pay for equal work." This marked a significant shift from the previous haphazard system, laying the foundation for the structured GS system we know today. Before this, federal salaries were often inconsistent and subject to political influence. The Act sought to create a more equitable and transparent compensation structure.
Over the decades, the GS pay scale has undergone numerous revisions and adjustments, reflecting changes in economic conditions, labor markets, and government priorities. The GS system is designed to be flexible, adapting to inflation and other economic factors through annual adjustments and locality pay differentials. Understanding these historical changes is crucial to appreciating the complexity and the rationale behind the current structure of the GS system.
The GS pay scale's importance lies in its role in attracting and retaining qualified individuals in the federal workforce. By offering competitive salaries and benefits, the GS system aims to ensure that the government can attract the talent necessary to perform its vital functions. The structured progression within each grade and step offers employees a clear path for career advancement and provides incentive for improved performance and longevity.
However, the GS pay scale also faces challenges. One significant issue is the increasing disparity between federal salaries and those in the private sector, particularly for highly specialized positions. This can make it difficult for the government to compete for top talent in fields like technology and engineering. Maintaining the competitiveness of the GS system while ensuring fiscal responsibility remains a key challenge.
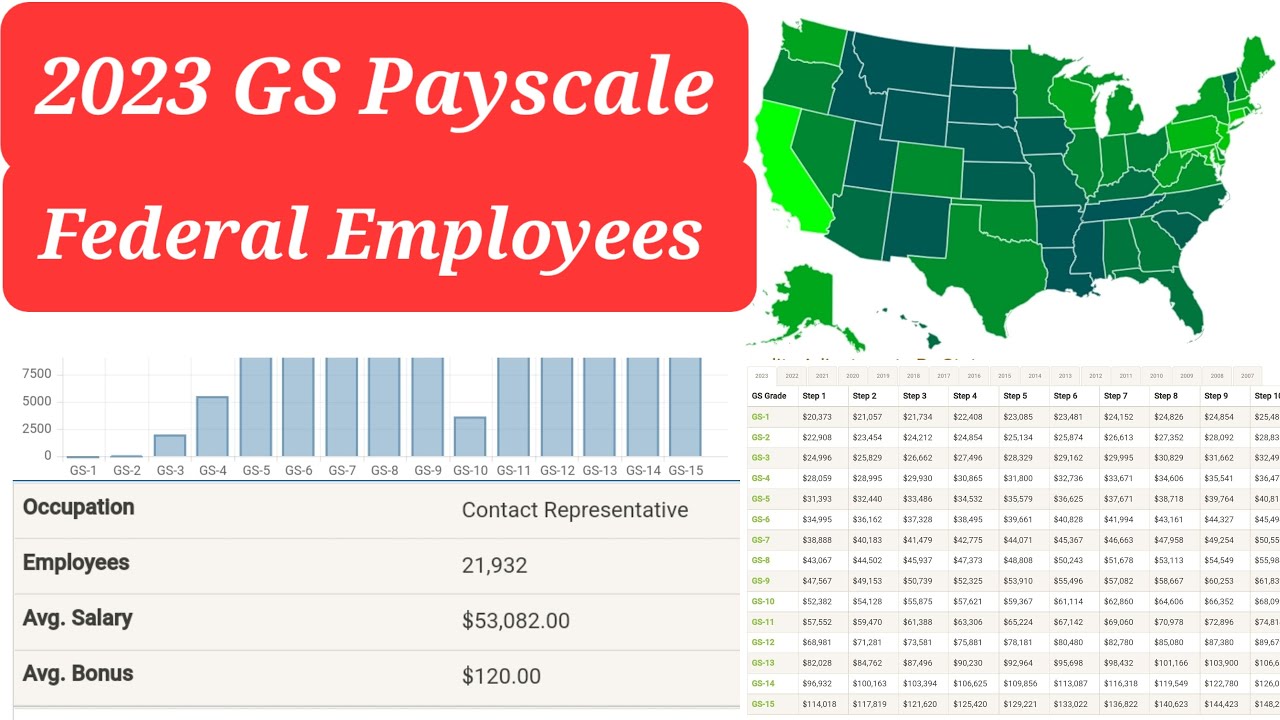
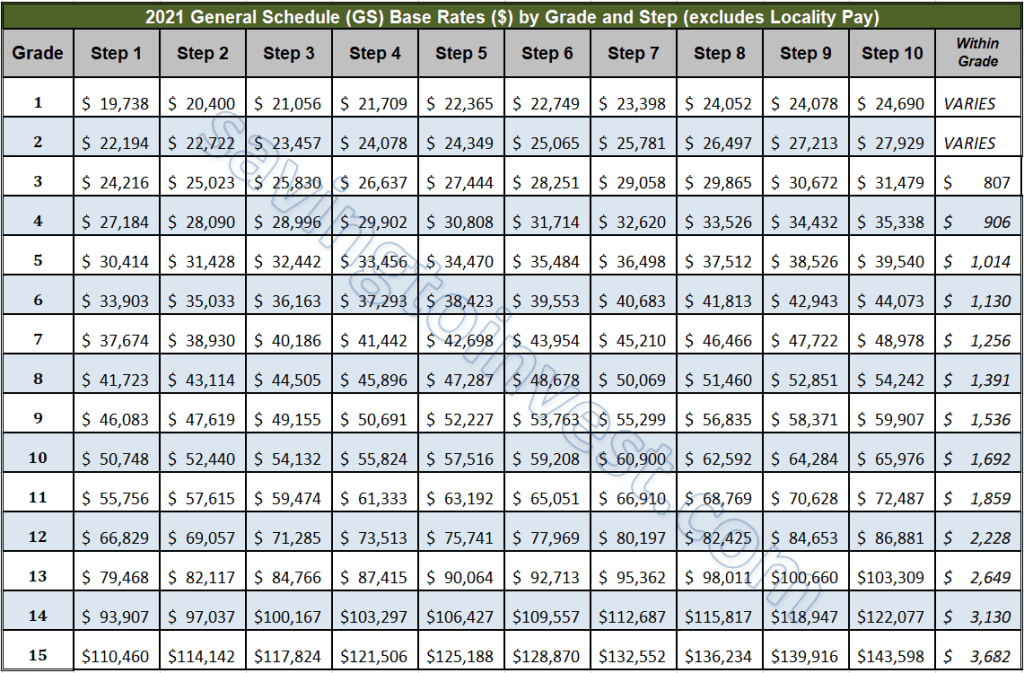
The GS pay scale is divided into 15 grades (GS-1 to GS-15), with each grade further divided into 10 steps. Each step within a grade represents an incremental increase in salary. For example, a new employee typically starts at step 1 of their assigned grade, and progresses through the steps based on performance and time in service.
One benefit of the GS system is its transparency. The salary tables are publicly available, making it easy for employees and potential applicants to understand the compensation structure. This transparency promotes fairness and allows individuals to make informed career decisions.
Another benefit is the predictability of the GS pay progression. Employees know what their potential earnings can be based on their grade and step, allowing them to plan their finances accordingly. This predictability provides stability and contributes to job satisfaction.
A third benefit is the portability of the GS system. Employees who change federal agencies can often maintain their grade and step, ensuring continuity in their compensation and career progression.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the GS Pay Scale
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Transparency and Predictability | Potential Salary Gaps with Private Sector |
| Structured Career Progression | Limited Flexibility in Addressing Specific Skill Shortages |
| Portability across Federal Agencies | Complexity of Locality Pay Adjustments |
Navigating the intricacies of the GS pay scale can be challenging. OPM's website is an invaluable resource for understanding the system's details.
Understanding the GS pay scale history is vital for federal employees and those considering a career in public service. The system, while complex, provides a structured and transparent framework for compensation. As the federal government continues to adapt to a changing world, the GS system will likely undergo further revisions to maintain its effectiveness in attracting and retaining the best talent. Staying informed about these changes will be crucial for anyone seeking a successful career in the federal government.
Unlocking serenity the sherwin williams graceful gray aesthetic
Behr stain review does behr stain live up to the hype
Aesthetic notebook decorating ideas