Ever wondered how to get that perfect shade of brown? Whether you're an artist, a DIY enthusiast, or just curious about color theory, understanding how to create brown opens up a world of possibilities. This guide delves into the fascinating world of brown hues, exploring different methods, historical contexts, and practical applications.
Creating brown isn't as simple as grabbing a tube of paint. It's a process of blending, experimenting, and understanding the interplay of colors. From rich chocolates to earthy siennas, the spectrum of browns is vast and diverse. This exploration into creating brown shades unveils the secrets to achieving the exact hue you desire.
The art of producing brown has a rich history, deeply intertwined with the development of pigments and dyes. Early humans utilized natural materials like earth pigments, burnt umber, and plant extracts to create brown hues for cave paintings and decorations. Over time, the techniques evolved, incorporating synthetic pigments and sophisticated mixing methods. Understanding this historical context provides a deeper appreciation for the complexity and versatility of brown.
The importance of brown in various fields cannot be overstated. In art, it represents stability, grounding, and natural beauty. In design, it adds warmth and sophistication. From fashion to interior decor, brown plays a crucial role in creating a balanced and aesthetically pleasing environment.
One of the main issues with creating brown is achieving consistency and the desired shade. Various factors, including the type of medium (paint, dye, ink), the quality of pigments, and the mixing process, can influence the final result. This guide will address these challenges, providing practical tips and techniques for consistent and predictable brown hues.
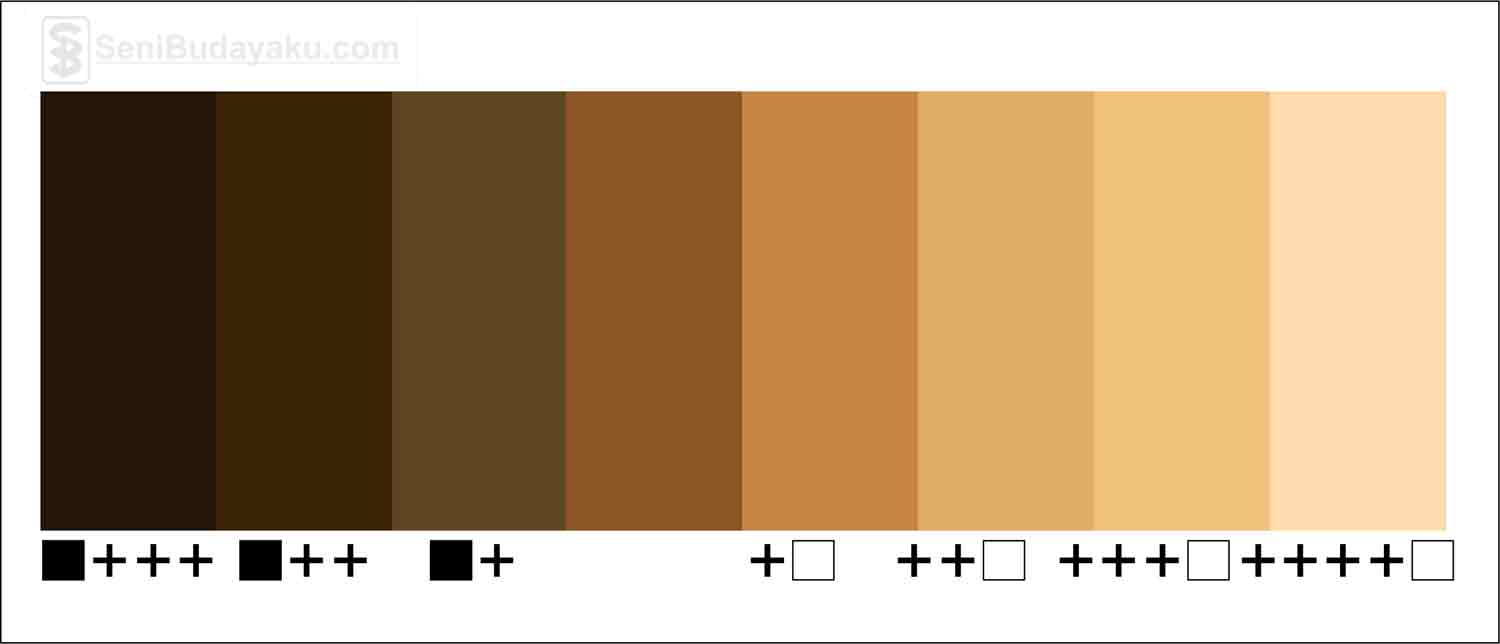
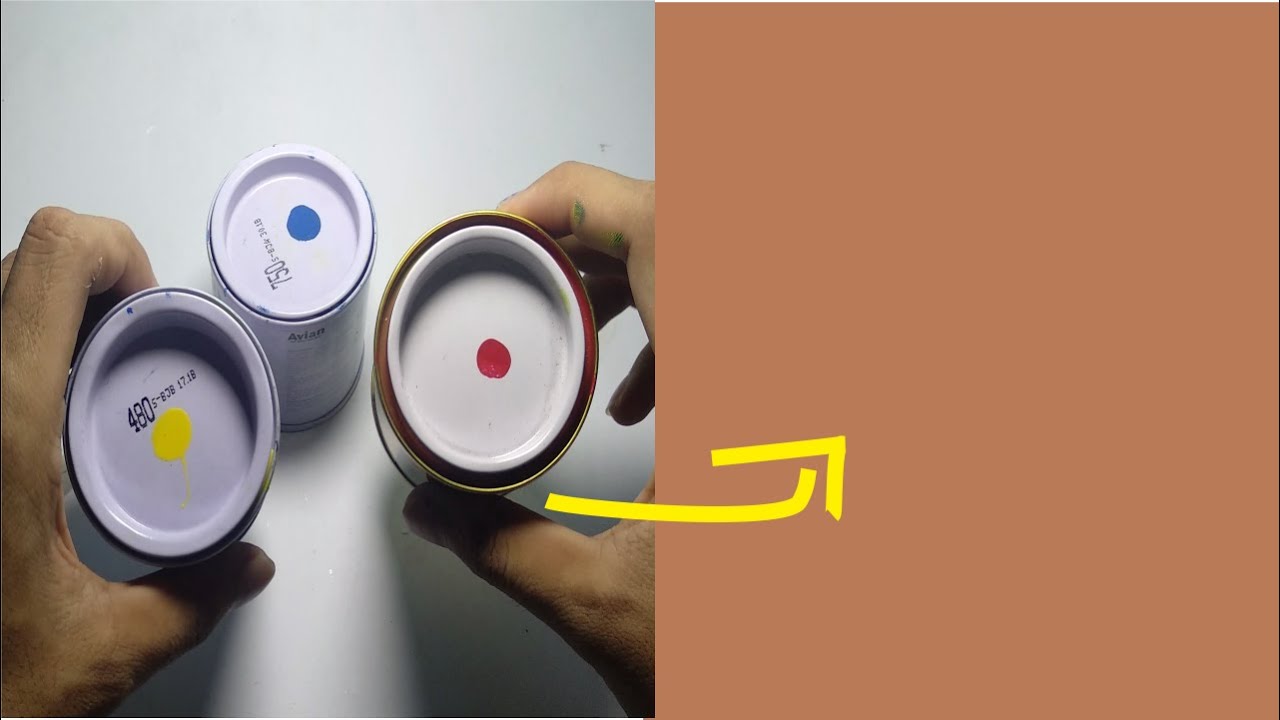
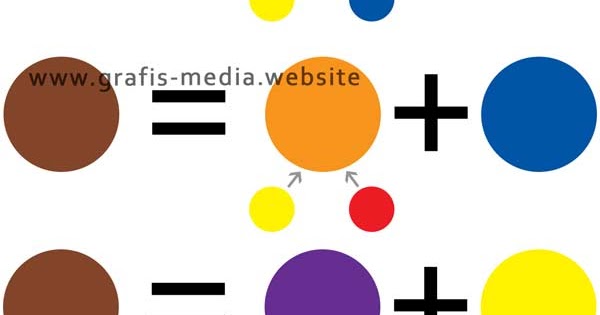
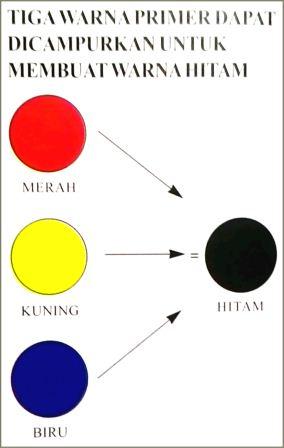
The most common method of producing brown involves mixing primary colors: red, yellow, and blue. By adjusting the proportions of these colors, you can create a wide range of brown shades. Adding black or white can further modify the intensity and value. For instance, more red and yellow will result in a warmer brown, while adding blue will create a cooler, more muted tone.
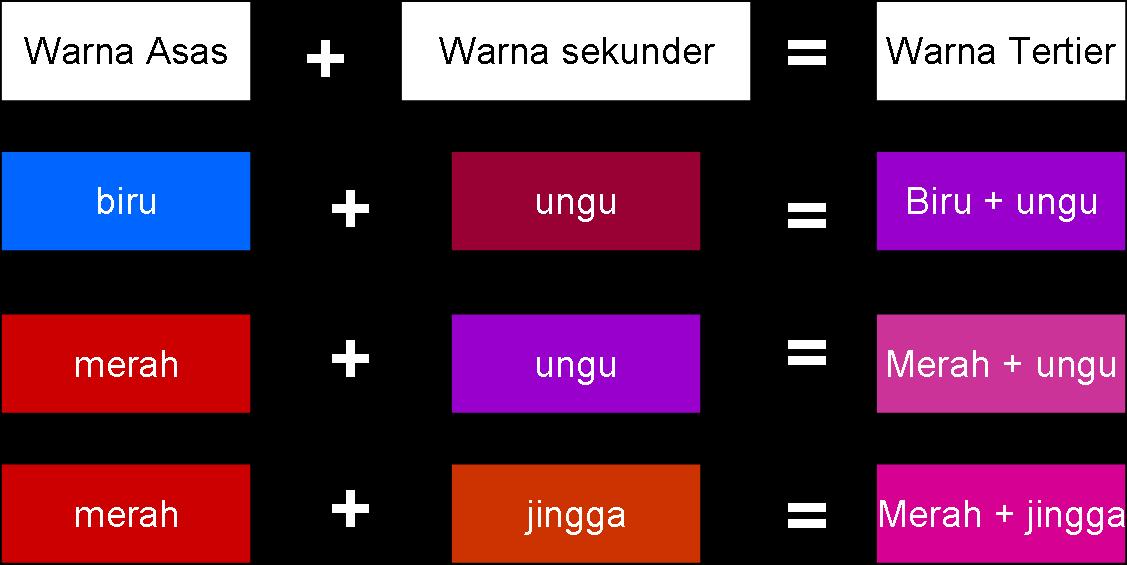
Beyond primary colors, brown can be achieved by mixing complementary colors, such as orange and blue, or red and green. Experimenting with different color combinations allows you to explore the nuances of brown and discover unique shades. Natural dyes, derived from plants, minerals, and insects, also offer a vast array of brown hues. For example, walnut husks create a rich, dark brown, while onion skins produce a lighter, more golden brown.
Creating your own browns has several benefits. First, it offers greater control over the final hue, allowing you to perfectly match a specific color palette. Second, it expands your understanding of color theory and mixing techniques. Lastly, it can be more cost-effective than relying solely on pre-mixed browns, especially for artists and crafters who use large quantities of paint or dye.
To successfully mix brown, start with small amounts of paint and gradually add more color until you achieve the desired shade. Use a palette knife or mixing stick to ensure thorough blending. Keep track of the color ratios for consistent results. Test the mixed brown on a small piece of paper before applying it to your final project.
For a warm brown, try mixing red, yellow, and a touch of blue. For a cooler brown, increase the amount of blue. Add black to darken the brown and white to lighten it.
Understanding color theory and the interplay of different pigments is crucial for consistent and predictable results. Practice and experimentation are key to mastering the art of creating brown.
FAQs:
1. What are the primary colors used to make brown? Red, yellow, and blue.
2. Can I make brown with complementary colors? Yes, for example, orange and blue, or red and green.
3. How do I darken a brown? Add black.
4. How do I lighten a brown? Add white.
5. What are natural sources of brown dyes? Walnut husks, onion skins, coffee grounds.
6. How do I achieve consistent brown hues? Keep track of color ratios and test on a sample before applying.
7. What are some common uses for brown in art and design? To represent stability, grounding, warmth, and natural beauty.
8. How does the history of brown pigment relate to its current use? Early methods using natural materials influenced the development of synthetic pigments and modern mixing techniques.
In conclusion, creating brown is more than just mixing colors; it's an exploration of the interplay of pigments and an understanding of color theory. From ancient cave paintings to modern design, brown hues have played a crucial role in human expression and aesthetics. By mastering the techniques described in this guide, you can unlock the potential of brown and achieve the perfect shade for your artistic endeavors, DIY projects, or any creative pursuit. Embrace the versatility of brown and let it enhance your creativity.
Unlocking the road your guide to semi trucks for rent
The curvy conundrum decoding male attraction
Carhartt xlt hooded sweatshirts the ultimate guide