Ever wondered how some of the heaviest machinery in the world operates with such fluid precision? From construction cranes lifting tons of steel to agricultural equipment smoothly tilling fields, the power behind these movements often lies in a deceptively simple yet powerful technology: belt-driven hydraulic pump systems. These systems are the unsung heroes of countless industries, silently and efficiently providing the muscle for a wide range of applications.
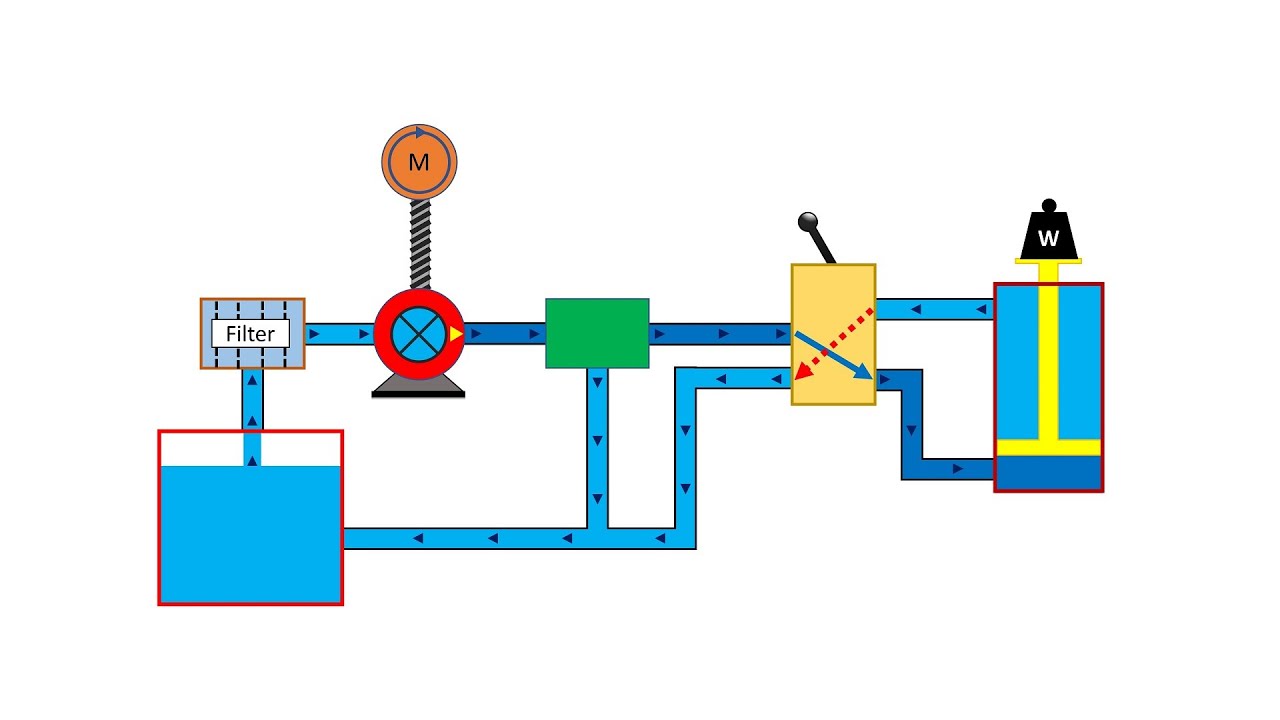
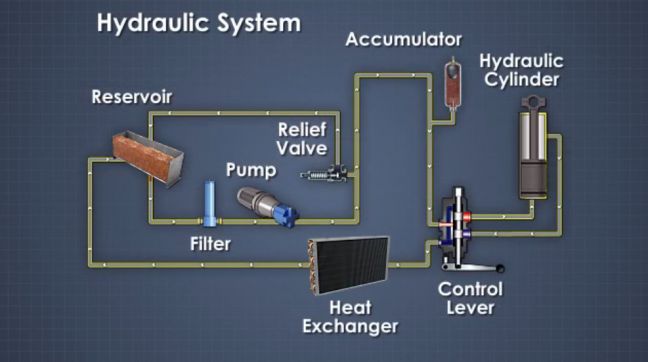
Belt-driven hydraulic pumps represent a clever combination of mechanical power transmission and fluid power. They essentially harness the rotational energy of an engine or motor, transferring it via a belt to a hydraulic pump. This pump then converts the mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, generating the flow and pressure needed to power hydraulic actuators, like cylinders and motors, which ultimately perform the work.
The versatility of belt-driven hydraulic pump systems stems from their adaptable nature. The ability to adjust the belt drive ratio allows for fine-tuning the pump speed and, consequently, the hydraulic system's output. This makes them suitable for applications requiring varying power demands, contributing to their widespread adoption across various sectors. Imagine a log splitter effortlessly slicing through thick wood – the controlled force enabling this precise operation is likely generated by a belt-driven hydraulic system.
Delving into the history of belt-driven hydraulic systems reveals an interesting journey of continuous improvement. While the fundamental principles of hydraulics date back centuries, the integration of belt drives for powering hydraulic pumps marked a significant advancement. This combination provided a flexible and efficient means of power transmission, propelling the development of more sophisticated hydraulic machinery.
These systems are essential for many industries because they provide a reliable and controllable source of power for heavy-duty applications. However, like any mechanical system, belt-driven hydraulic pumps can encounter issues. Common problems include belt slippage or wear, pump leaks, and cavitation. Regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting are crucial to ensure the system's longevity and optimal performance.
Belt driven hydraulic pump systems operate by utilizing a belt to connect a motor to a hydraulic pump. The motor’s rotational energy is transmitted through the belt, causing the pump to rotate. This generates the flow of hydraulic fluid needed to power hydraulic actuators. For example, in a car lift, the belt-driven pump system generates the pressure needed to raise and lower the vehicle.
One key benefit of these systems is their flexibility. The speed ratio between the motor and the pump can be adjusted using different pulley sizes. This allows for optimization of the pump's output based on the specific application. Another advantage is their relative simplicity, which translates to easier maintenance and repair. Finally, belt drives offer a degree of shock absorption, protecting the pump and motor from damage due to sudden load changes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Belt Driven Hydraulic Pump Systems
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Flexibility in speed and power output | Potential for belt slippage or wear |
| Simplified maintenance and repair | Lower efficiency compared to direct-drive systems |
| Shock absorption protects components | Space requirements for belt and pulleys |
Implementing a belt driven hydraulic pump system effectively requires careful consideration of several factors. Proper belt tension is critical. Too loose, and the belt slips; too tight, and it puts excessive strain on the bearings. Selecting the correct belt type is also important, considering factors like power requirements and environmental conditions. Regular inspection and maintenance are essential for preventing breakdowns and ensuring longevity.
Belt-driven systems are used in various applications, including agricultural machinery, construction equipment, and industrial presses. Understanding the unique demands of each application is crucial for selecting and implementing the appropriate system.
Common challenges include belt slippage, pump leaks, and fluid contamination. Solutions include proper belt tensioning, regular seal checks, and fluid filtration.
FAQs: What are the key components? How do I maintain it? How do I troubleshoot common issues? What are the different types of pumps used? What are the safety precautions? What are the applications? How do I choose the right belt? What factors affect efficiency?
Tips: Regularly inspect the belt for wear and tear. Ensure proper alignment of pulleys. Use the correct type and viscosity of hydraulic fluid. Monitor system pressure and temperature.
In conclusion, belt-driven hydraulic pump systems play a vital role in powering countless machines and processes across various industries. Their adaptability, flexibility in power output, and relative simplicity make them a reliable and efficient choice. While challenges like belt slippage and maintenance requirements exist, understanding best practices and implementing preventative measures ensures optimal system performance and longevity. From the construction site to the farm, the seamless operation facilitated by these systems contributes significantly to our modern world. Investing time in understanding and maintaining these systems ensures their continuous and efficient operation, enabling us to continue leveraging the power of hydraulics for years to come. By understanding the intricacies of these systems, we can harness their power efficiently and effectively, driving progress and innovation across various sectors.
Sss class ranker manga 86 a triumphant comeback
Diy boat lift designs save money and protect your vessel
Unlocking the power of bolt hole circle patterns