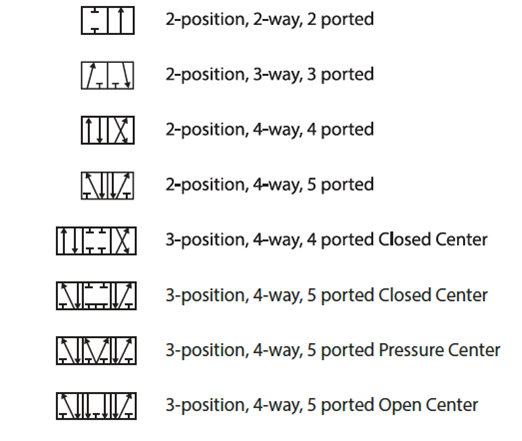
Imagine a world without automated machinery, where complex tasks rely solely on human effort. The rise of automation has transformed industries, and at the heart of many automated systems lies the power of pneumatics. Understanding pneumatic symbols and their associated functions is crucial for designing, operating, and maintaining these systems effectively.
Pneumatic systems harness the power of compressed air to control and actuate mechanical components. These systems are prevalent in various industries, from manufacturing and packaging to robotics and automation. However, the complexity of these systems necessitates a standardized language for representation – pneumatic symbols. These symbols serve as a visual shorthand, enabling engineers and technicians to interpret and troubleshoot pneumatic circuits efficiently.
Pneumatic schematic diagrams, much like blueprints for a building, provide a visual representation of the interconnected components and the flow of compressed air within a system. They employ a standardized set of symbols, each corresponding to a specific pneumatic function, such as directional control valves, actuators, pressure regulators, and air filters. This standardization ensures clear communication and collaboration among professionals working with pneumatic systems across different regions and industries.
Decoding these pneumatic diagrams requires a solid understanding of the symbols and their associated functions. This knowledge empowers technicians to diagnose malfunctions, implement modifications, and optimize system performance. The ability to interpret pneumatic schematics is an invaluable asset for anyone working with automated machinery.
Furthermore, the adoption of standardized pneumatic symbols is deeply rooted in the history of industrial automation. As pneumatic systems grew in complexity, the need for a common language became evident. Organizations such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) played a vital role in developing and promoting the use of these standardized symbols, leading to enhanced safety, efficiency, and interoperability in pneumatic system design and implementation.
Pneumatic symbols represent various components, including directional control valves (used to control airflow direction), actuators (like cylinders that convert compressed air energy into mechanical motion), and flow control valves (regulating the speed of actuators). For example, a single-acting cylinder symbol shows a piston within a cylinder with a single port for air inlet, indicating its single-directional movement.
Benefits of understanding these symbols include: 1) Efficient troubleshooting: Quickly identify faulty components within a system. 2) Improved design and modification: Enable engineers to create and modify pneumatic circuits with ease. 3) Enhanced communication: Facilitate clear communication among technicians and engineers.
To master pneumatic symbols, start with basic symbols and gradually progress to more complex ones. Practice reading and interpreting simple pneumatic circuits and gradually move on to larger, more intricate systems. Several online resources, textbooks, and training programs are available to guide you.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Pneumatic Symbols
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Clear communication | Initial learning curve |
| Efficient troubleshooting | Potential for misinterpretation if not followed correctly |
| International standardization |
Best practices include using clear and concise diagrams, adhering to ISO standards, and properly labeling all components. Real-world examples include robotic arms in assembly lines, automated packaging systems, and pneumatic presses. Challenges in using pneumatic symbols include keeping up with evolving standards and ensuring proper interpretation. Solutions involve ongoing training and utilizing updated resources.
FAQs: 1. What is a directional control valve symbol? (A symbol depicting the flow paths of compressed air.) 2. How does a double-acting cylinder symbol differ from a single-acting one? (It shows two ports, indicating air inlet and outlet for both directions of piston movement.) And so on with additional FAQs about common symbols and their functions.
Tips and tricks include using software tools for drawing pneumatic diagrams and practicing regularly with different circuit examples. This will help reinforce your understanding of pneumatic symbols and their applications in real-world systems.
In conclusion, understanding pneumatic symbols and functions is paramount for anyone involved in the design, operation, or maintenance of automated systems. These symbols provide a universal language for interpreting pneumatic schematics, enabling efficient troubleshooting, improved design modifications, and enhanced communication among professionals. Mastering these symbols opens doors to a deeper understanding of complex automation processes, enabling innovation and optimization in various industries. By embracing standardized symbols and consistently following best practices, you can contribute to the seamless integration and efficient functioning of pneumatic systems in a wide range of applications. Explore the available resources and commit to continuous learning to fully unlock the power of pneumatics. This knowledge is an essential tool for any aspiring engineer or technician in the field of automation.
Decoding aarp medicare supplement insurance
Urea to nitric acid a deep dive into the innovative process
Unlocking the toyota rav4 automatic transmission a deep dive